
‘Freedom, understood concretely, is a civilizational, not a natural, construct. This essentially conservative argument could provide the very basis for the continuation of a certain political tradition without which we, modern souls, would live in a much more cruel and inhumane world.’
‘Ortega’s image of what members of his ideal elite should be like derives from his wider philosophy. His spells at German universities made him initially a fervent neo-Kantian who, seeing the world through the lens of transcendental idealism, believed in the objective reality of the Platonic triad of truth, goodness, and beauty, and that this should form the basis of one’s life and education…’

‘The Third Budapest School strives to debate the one-sided, analytical, progressive, nihilistic aspirations that dominate American intellectual life, and to cultivate initiatives based on classical European philosophy. It does this by stimulating the formulation of important questions: in contrast to the activist Leninist “What is to be done?”, the Third Budapest School holds that the preeminent question is: “What is to be asked?” This means that the most important measure of all intellectual activity is reality. ’

‘There is one sense in which Aquinas certainly did not believe in worlds. This is the sense in which certain Greek philosophers held that there is an infinity of worlds…Aquinas asserts what he calls the “unity of the world”. He claims, too, that the very concept of world denotes a “unity of order”.’

Policies such as pro-family tax cuts, housing programmes, child benefits etc., all resulting in a kind of family income system that aims to reduce the harm inflicted on families by a Ricardian conception of the economy (which, obviously, cannot be completely overthrown, since we cannot go back to the lifestyle of preindustrial societies), should become a vital part of conservative policies, and should be seen as such in the modern conservative movement, as Allan Carlson pointed out in his Third ways.

‘On our part, we doubt that “history of ideas” as a methodologically coherent discipline existed in Hungary between the two world wars…Nevertheless, their work is undoubtedly a prime example of an attempt at the creation of a conservative-oriented social science. The history of ideas is, in fact, a philosophy of history that takes into account factors that transcend matter, and through a specific research methodology is able to grasp and evaluate the processes that take place “behind” the surface of purely material social phenomena.’
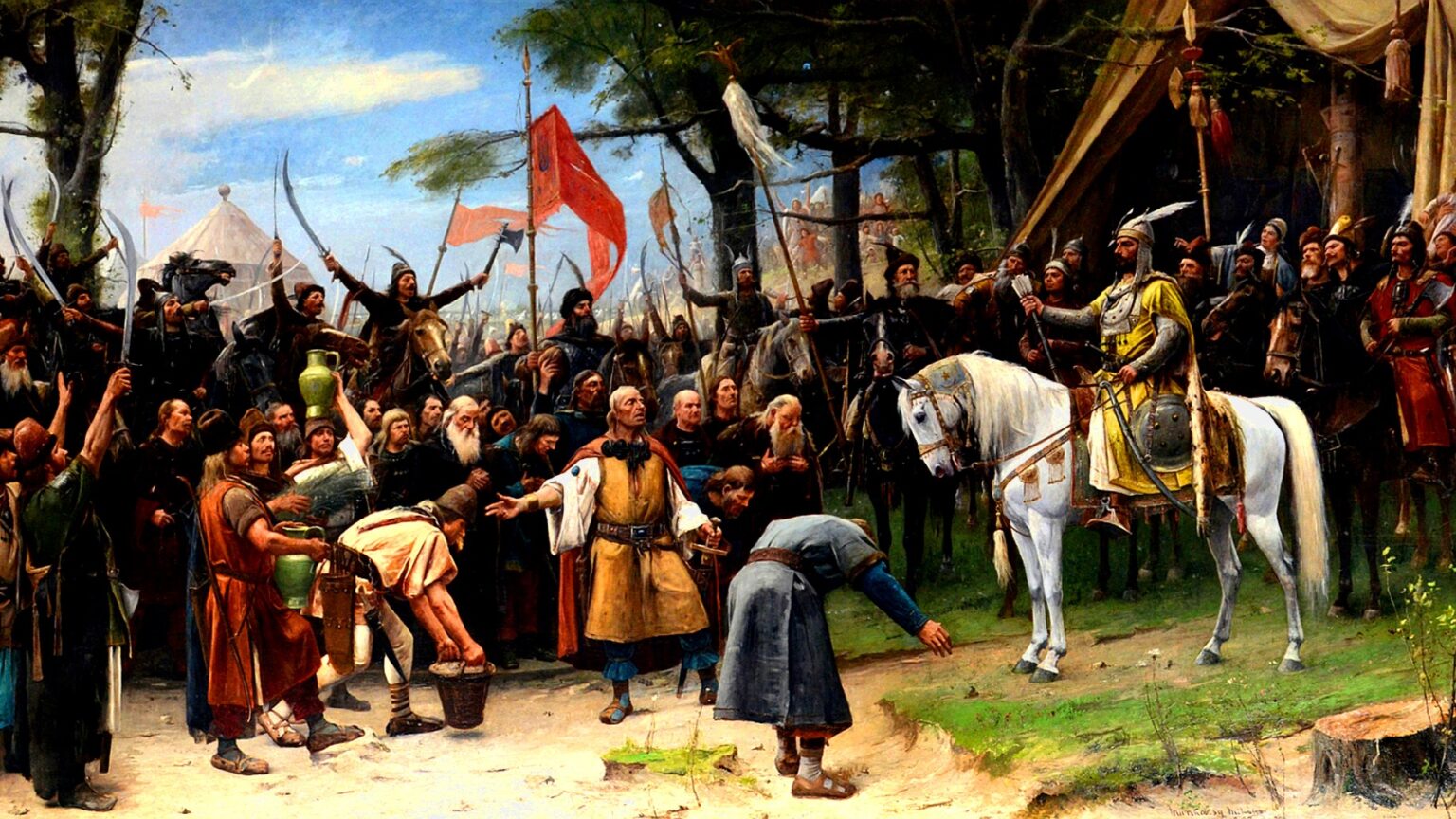

‘Linguistic–ethnic nationalism is the quintessential negative (in Joó’s parlance, “imperialist”) nationalism, a nationalism insensitive to qualitative differences or to more elevated spiritual concepts of the state, such as the unifying “Hungarus consciousness” of the nomadic empire’s supranationalism, which derives from the dynasty’s divinely-derived spiritual unifying power.’

‘The most important distinguishing feature of the Hungarian national ethos and Hungarian nationalism, according to Joó, is that the Hungarian nation’s leitmotif of Steppe origin survived the foundation of the Christian state, and even survived the Middle Ages, synthesizing it with Christianity. In Western Europe, however, a very different kind of nation-building took place. Charlemagne’s brief attempt at empire-building, i.e. his efforts to renew the Roman Empire on a Christian–Germanic basis, essentially quickly failed.’
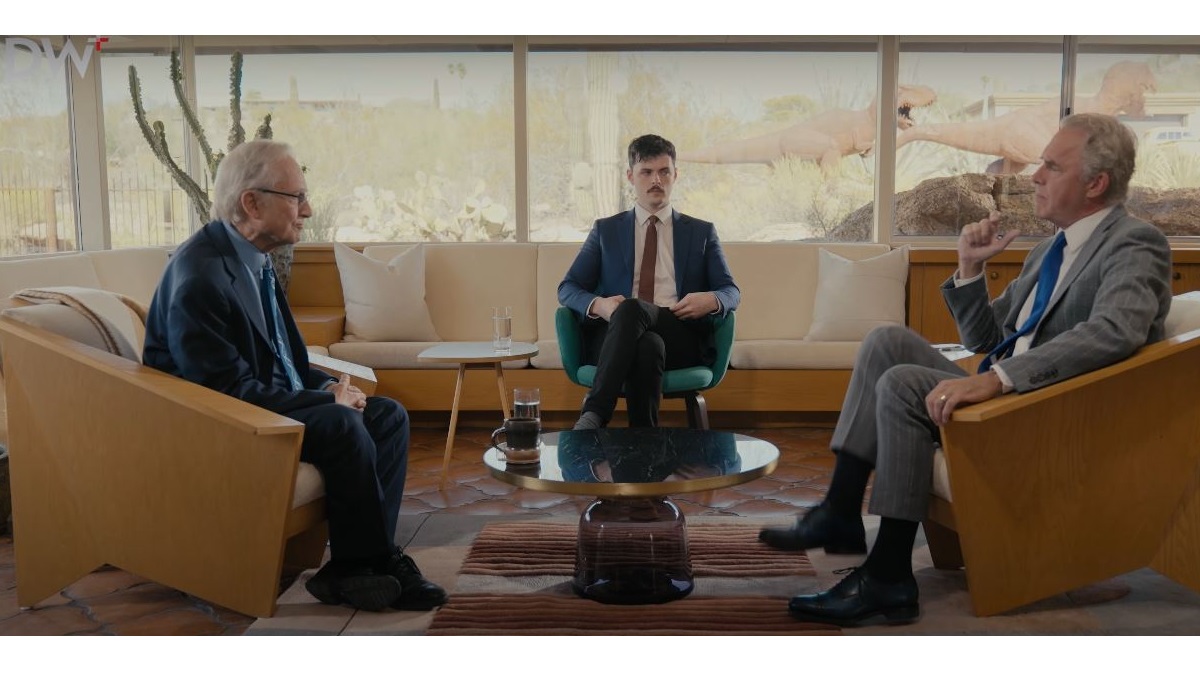

Dr Jordan B Peterson has recently had a public discussion with evolutionary biologist Dr Richard Dawkins, one of the most prominent figures of the popular atheist movement of the early 2000s. The two philosophers touched on subjects such as Jesus Christ’s birth of a virgin mother and his resurrection, the philosophical foundation for the modern scientific enterprise, and many more intriguing questions.

‘As a committed Protestant, Joó emphasized the primacy of “spirit” over matter in almost all his writings, but he failed to take into account that religion and “spirit” do not always overlap, and religiosity itself simply becomes ineffective if so-called religious people view the world on the same premises as their atheistic and materialistic counterparts.’

‘As modern consumer society has made consumption the root of identity, man has become a prisoner of the constant renewal of consumer demands…Contrary to early capitalist societies, people have completely reduced themselves to the self-as-consumer. The short excitement that accompanies consumption is all that modern man has left.’
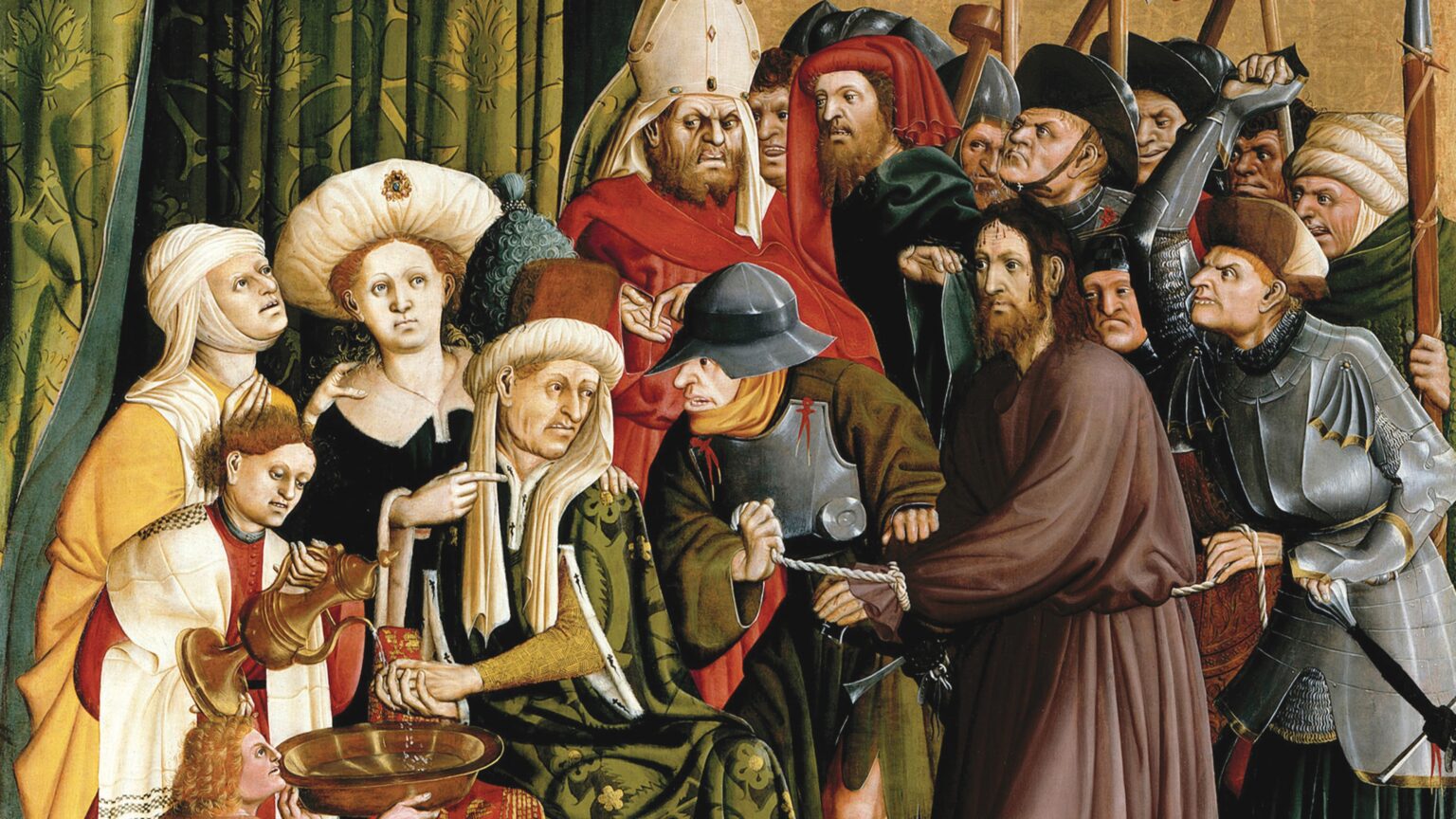

‘Coming up with an authoritative definition of conservatism is not an end in itself so much as a sort of ritualistic pursuit, which we perform expecting some change from it along the lines of a deeper understanding of our past, our present, and the mysteries of the human species and the world. There are any number of ways in which the history of conservative thought could be written, if only as a story of the attempts at grasping the very notion of conservatism.’

‘There can be no question that Thomas Molnar’s thought was often driven by a confrontation with the intensified secularist, materialist, and anti-religious ideological tendencies following the socio-historical and ideological period of the eighteenth century. He sought the roots of modern political philosophies such as liberalism and Marxism.’
‘Today, the expansion of the state apparatus…continues, but is approaching its culmination. In this spirit, that is, the announcement of the ‘‘fourth industrial revolution’’ and ‘‘digitalization’’, all of which fit into the logic of rationalization and rationalism, the world is becoming more and more virtual, and technology is becoming more and more totalitarian, a new mechanism of control.’
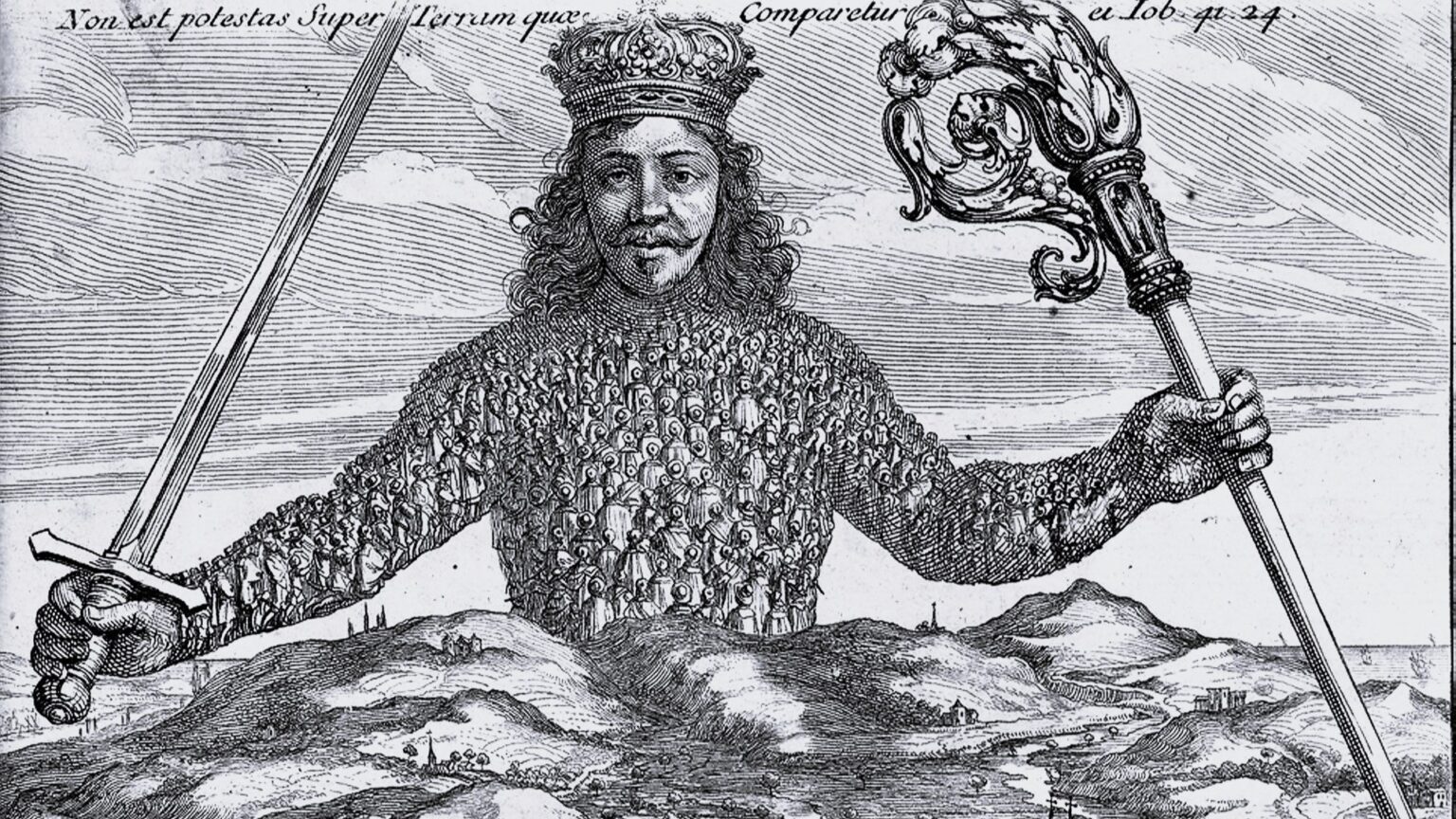

‘What can the modern conservative politician do in the face of such a Leviathan, which he did not create? He has two choices: either he retires and no longer wants to be in politics, or he tries to ride this sea serpent, he tries to use the power of the monster to ‘‘take’’ society in a direction that is contrary to the direction of the alleged progress.’
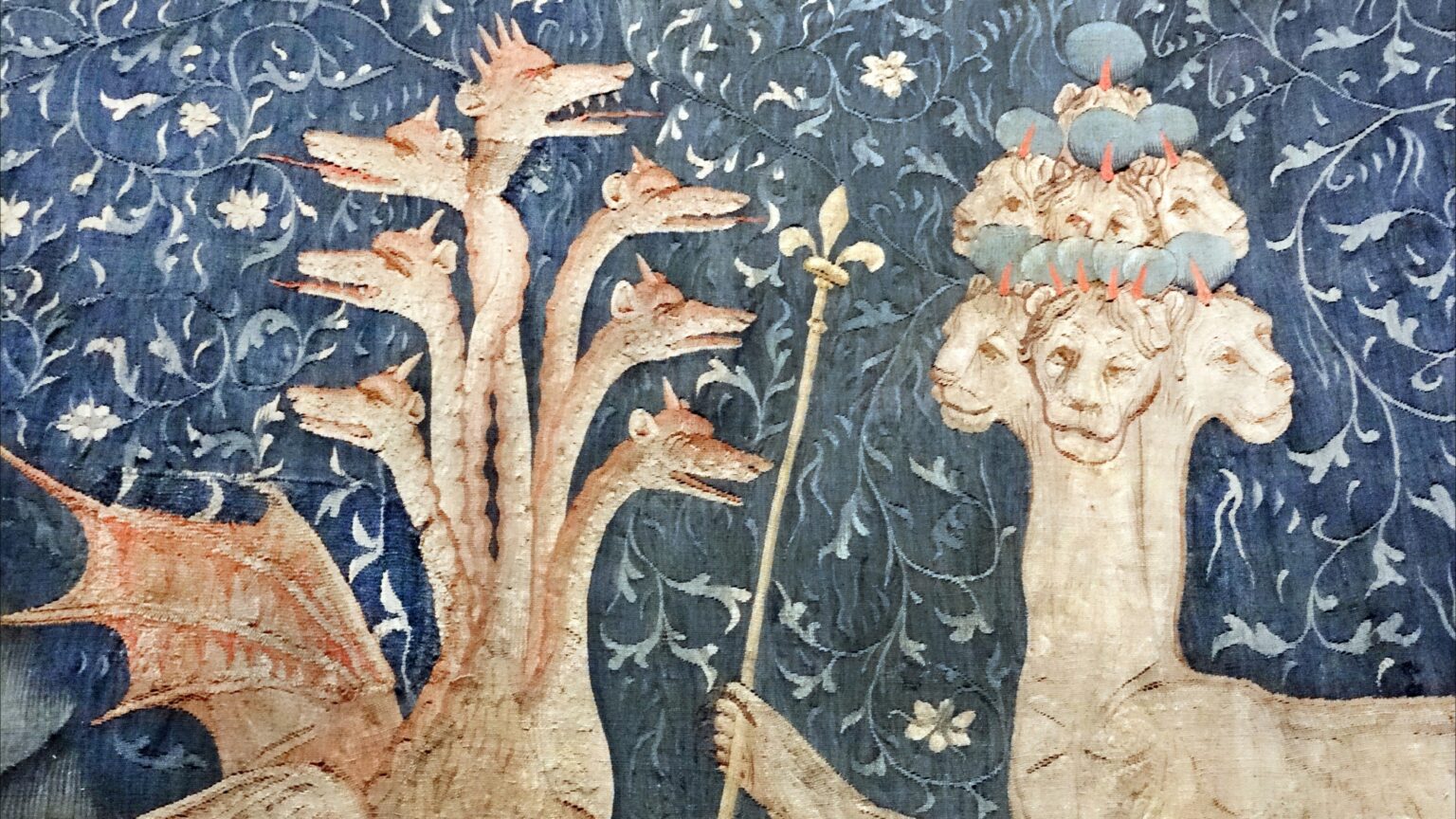

‘If we accept the existence of transcendence as conservatives, we must also accept that everything that is outside the transcendent is sui generis subject to change. Change— and thus clearly also the fact of decline or progress—is made possible by transcendence as everything else ‘‘in’’ the world. The existence of the ‘‘Eternal’’—this is the particular knowledge that is the most important part of the ‘‘wisdom of the ancestors’’ and it is what the moderns have forgotten.’

‘I believe that the true ontological essence of conservatism is contained in the definition: conservatism is the making present of actuality. In this way, conservatism is bound both to the particularities of specific belonging cultures and to the wider belonging civilization…Conservatism as a political philosophy arises when the address of the aforementioned actuality is threatened.’

‘To maintain social order, legitimate authority needs to be guarded so that popular sovereignty cannot derail in a popularity contest, which we witness today, for example in the American elections. It means that our leaders need to be honest about the human condition as well as provide a stability in which each person, in line with their talents and destiny, can thrive.‘

‘Space and time represent the two archetypes of political existence…Space inherently belongs to the polis, the starting point of political ‘residence’ (at least in the European cultural circle), and time belongs to the ship, the instrument of the ‘free movement of capital and labour’; the ship is an ancient invention but it is also—only developed later in time—a symbol of progression, change and technological dominance.’

‘It is rarely taken into account that forcing a general expansion of education also means levelling. And if something is extended in a general and obligatory way, then it will be quantitative rather than qualitative. If we imagine all of this in a school system that is universally compulsory for everyone, then according to today’s well-known hierarchization of knowledge, only knowledge that can be (easily) validated in the so-called ‘labour market’ will be truly appreciated.’

‘Just as liberalism did not succeed in transforming people after socialism, neither did the competing anti-liberal, post-Christian, nihilistic trends. The solution is certainly not political or movement-based: those had already failed by the middle of the twentieth century.’

‘Christian realism is not unprincipled power politics or mere pragmatism, but the intelligent use of power and politics for the sake of representing Christian ideas and the common good (bonum commune), within the bounds of worldly political constraints.’
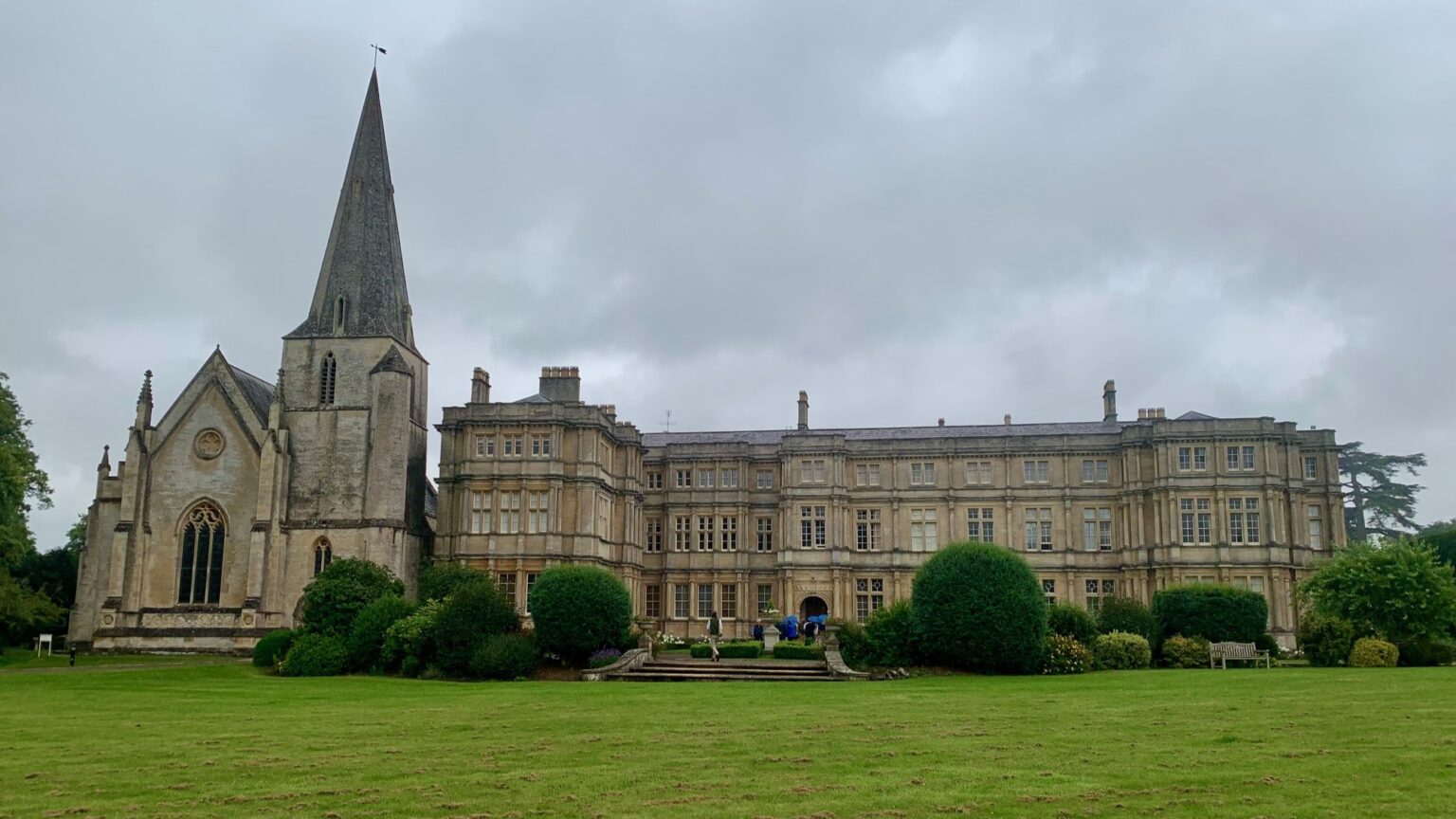

‘The programme took place in the idyllic settings of the Royal Agricultural University in the Cotswolds and Sundey Hill Farm, where Sir Roger lived and worked for three decades. The week’s agenda was filled with intellectually stimulating lectures, vibrant discussions, and culturally rich activities that provided insight into Sir Roger’s life and work as well as into broader conservative values.’

‘Europe finds itself at a critical situation, faced with a fundamental choice between unity in progressivism or sovereignty in diversity…Central to this decision is the recognition of Europe’s intrinsic diversity, rooted in centuries of history, cultural exchange, and shared heritage. This diversity, inherently European, forms the essence of the continent’s identity and should be cherished and preserved. Importantly, efforts to import diversity from external sources often lead to fragmentation and discord, rather than enriching European society.’

‘It might not be as explicitly visible as substance abuse, but below the surface, we are all struggling with our own imperfection and “sinfulness”. We all let our subjective anxiety overwhelm us and tempt us into a destructive state. Kierkegaard perfectly described how we fall for this anxiety: “Anxiety may be compared with dizziness. He whose eye happens to look down into the yawning abyss becomes dizzy.”’

‘In today’s culture, one has to explain how the modern existential paradigm does not hold the truth to sustain a prosperous life or society. With radical and individualistic generations being raised, nothing is more effective than to point out how existential nihilism does not bring happiness, meaning or prosperity. Cheap surface moralism should therefore be replaced by a transcendental framework of meaning and purpose.’

‘The doubtful mind has been persuasive and embedded in modern Western culture. Therefore, it is important to understand the underlying psychological falsehood. Radical doubt only works as an abstract confusion which paralyses people into a void of distress. Additionally, doubt enhances the inability to make decisions and take responsibility for your actions. To be in a state of the doubtful mind, is to be in a state of looking back.’

‘But national consciousness is precisely the origin of modern democracy and is still crucial for organizing democratic solidarity. Of course, nationalism can lead to a dangerous chauvinism which makes people believe that their nation has the right to bully others, but these cases are, fortunately, exceptional excesses. The big picture is that nationalism and modern parliamentary democracy emerged in the 19th century in intimate connection and presuppose each other.’

‘A successful republic, according to Machiavelli, is characterized by laws that are lived by rather than frequently amended. While no system of governance can achieve absolute perfection, a stable republic can achieve a functional balance. For him Rome serves as a historical exemplar of such a system, where laws were respected and adhered to, placing communal benefits above personal gain, thus prudently managing both public and private affairs.’

‘Before the term “liberal” became ideological, it referred to much more general, non-political characteristics: open-mindedness, generosity, and the like…Liberalism, however, marked the triumphant beginnings of modernity, which aimed to create a political morality called “the conception of rational choice as the generator of political order”.’

Hungarian Conservative is a quarterly magazine on contemporary political, philosophical and cultural issues from a conservative perspective.