
‘[T]he…West…has finally reached the Baudrillardian singularity, and become completely absorbed by a self-referential simulation that its own leaders have created. This simulation continues to insulate the leaders of the West, but as rays of underlying reality start to shine through the cracks in the edifice, most people conclude that our political systems are becoming increasingly “fake”.’

‘The mass man is incapable of making authentic, personal decisions in situations of crisis or autonomy. For this reason, he requires a leader—someone who can think, decide, and act on his behalf. This leader makes the mass man aware of his power through numerical superiority and conformity, shaping modern mass states.’

‘In the twenty-first century, it might be thought quixotic…to be highlighting ideas about the purpose of universities that have anything to do with conservatism…The dominance of a progressive liberal “idea of a University” should not, however, let us forget that there is a conservative “idea of a University” waiting in the wings and ready for the opportunity to reassert itself…’

‘In an age where a phone tells better time than any Rolex, watches are thriving—not despite their obsolescence, but because of it. They are beautiful, technical, embodied objects in an abstract and disposable world. They are the final adornment, the last private ritual, the culture of time made visible—and kept close to the skin.’

‘Leo XIII hinted…that Christians and non-Christians alike…can only benefit from natural law…because it “is universally valid apart from and above other more debatable beliefs, [and] constitutes the compass by which to take our bearings in legislating and acting, particularly on the delicate and pressing ethical issues that, today more than in the past, regard personal life and privacy.”’

‘China is looking for a new moral synthesis of its Confucian and Western political culture that could stabilize Chinese society and take its “positive union” to new heights. This could be one of the most constructive dialogues between China and the West. But as the influence of Marxism in China wanes, the moment for this dialogue could pass at any time. Let us not miss this exciting opportunity.’

‘Can Western nations hope to resurrect Western hegemony while remaining so dysfunctional domestically? Deeper still: are some of these domestic dysfunctions a direct result of their role in maintaining a liberal empire in its late stages? Viewed this way, the emerging multipolar world might…also present opportunities for cultural and political revitalization in the West.’

‘As conservatives, we understand that the world is a broken and imperfect historical place. We cannot go back in time, but we can focus on building a future that is more conscious of the dangers posed by the neo-Durkheimian order to local conservatism. To protect local conservatism and nourish its telos, we must argue for the restoration of national sovereignty…’

‘…the idea of a Creator conceived and represented in vulgar theological approaches as a quasi-human person is not only unacceptable today but also explicitly harmful to the contemporary expressions and life-opportunities of religion, fostering further denial and turning away in philosophically or scientifically trained minds.’

‘The idea of the survivability of death is a key problem, because in its light the whole of life takes on a completely different meaning: if it is possible, nothing else is more important than this; if it is not possible, nothing else is more important than maximizing power and profit in the short period of life on earth—which submerges all other goals.’

‘…the ideas of Pál Kecskés on education and pedagogy are fundamentally rooted in Christian social theory, which seeks to envision an ideal society from a Christian perspective. His reflections remain relevant today, in a time when individuals…have perhaps never had a greater need to understand education and formation as inherently social processes.’

‘In Hungary, unique master narratives have emerged over the centuries that live with us to this day. We can run into them everywhere in the most diverse segments of life: in culture, in education, even in politics. What exactly does the term master narrative mean and why is it so crucial to our lives and identities? What are the defining Hungarian master narratives?’

‘We must resist the anthropology that reduces our humanity to a commodity of flesh, an anthropology that hollows out our interiority, an ontology that will not permit that interiority to have any substantial existence. Our task is not to preserve or defend the West. If Camus is right, we are way past that point. Our task is to decolonize the West.’

‘It is no longer clear where the boundaries between nature and culture, human and non-human, artificial and natural lie. In the face of this great uncertainty, we need to rethink fundamental questions such as what the social order is. It is no exaggeration to say that we need to recreate our worlds on a planet where the very foundations of life are being called into question.’
‘Applying Christian theology and ethics to international relations is now an acutely important activity. The hopeful realism of Reinhold Niebuhr offers one way of recovering a Christian approach to the crisis that is hurtling towards our civilization at a terrifying speed. Niebuhr’s anthropological pessimism provides a foundation for his notion that nations can, and should, work towards a fragile justice.’
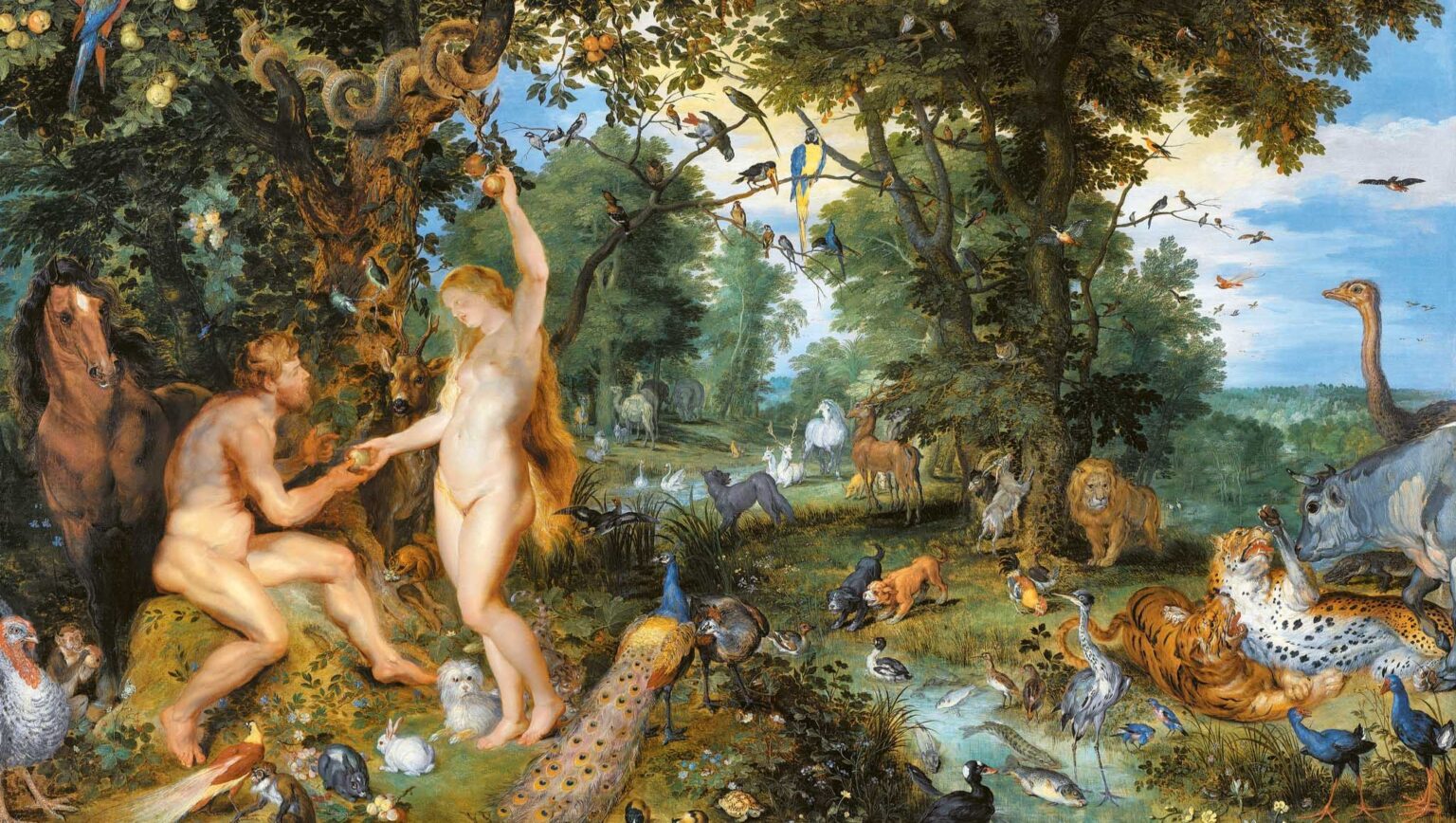

‘Orbán and the Fidesz leadership are seeking lasting change to Hungarian politics and culture. They recognize that pro-life and pro-family issues are not just legal disputes; they are culture-wide struggles, and they must be addressed as such. Hungarian conservatives are not surrendering on these issues, and they are not acting recklessly…the Orbán government’s family policies are prudent.’

‘According to Prohászka, in modernity the tradition of earlier, non-atheistic ages does not die out completely, so that modernity, despite its distinctness, also draws on expressions of earlier forms of cultural life. If a positive turn is to be made, this must be grasped first and foremost.’

‘Prohászka have perceived that the blaring confidence of progressivist thought reflected only its inner emptiness, its blindness, its superficiality, its logical and philosophical inconsistency. What follows from these “new principles” is, above all, a tragedy of human existence, more serious than ever before. It is the denial of the immortality (or the possibility of immortality) of the soul.’

‘As Márton Molnár puts it, “Prohászka’s work covers three major—closely related—themes: educational science and the history of education…the theoretical issues of the philosophy of culture; and the problems of the modern cultural crisis.” In this paper, we focus on this last area: the modern cultural crisis.’

‘Strauss points away from the modern project of progressive enlightenment and toward an individual ascent out of modernity. Neither of the two premodern ways of life, biblical or philosophic, partakes of the modern hope in social progress, nor in the late modern historicism that would confine all thought to its time and place and obscure eternity. The fruitful antagonism of the two pre-modern ways of life stands in sharp contrast to the failed modern synthesis.’

‘Without culture, Eliot argues, there is no point at all in being human, and it is culture that justifies the content of our existence on Earth for the generations that follow us. “Culture may even be described simply as that which makes life worth living. And it is what justifies other peoples and other generations in saying…that it was worth while for that civilisation to have existed.”’

‘Whether through Scripture, the teachings of the Church, or life experience, Christians learn that no relationship or physical place makes them truly at home. For Christians, it has always been challenging to find the right balance between our hope in Jesus Christ and His coming kingdom and our vocations as citizens, spouses…In their articles in The European Conservative, Audrey Unverferth and Rod Dreher highlight important points about family, community and home.’

‘According to the Chinese zodiac, 2025 is the year of the snake, which symbolizes change and transformation. It thus may not be a coincidence that Donald Trump, who campaigned on a promise to bring about drastic changes in Washington, commenced his second term as President of the United States in this epochal year.’

‘By rediscovering fundamental needs and values, we will eventually rediscover the need and motivation for having more children. This is a collective project that involves, first of all, ordinary people, philosophers, the church, artists, psychologists, and the government.’

‘People generally agree that no human society is “without culture”. The concept has been defined in many different ways. The first appearance of the term culture is attributed to Cicero, who used the word in the sense of “cultivation of the soul”…only at the beginning of the 19th century did it acquire the meaning that can be described as “learning and taste, the intellectual side of civilization”.’

‘Here the problem of postmodern thinking returns. If there is no truth, since everything is relative and free (but if there is an absolute truth, Derrida calls it totalitarianism), then in the marketplace of ideas, truth—since it does not exist—cannot stand out. If there is no truth, thus no lie, and no set of values, then anything can be disseminated in the public discourse of democratic countries, because there is freedom of speech.’

‘Politically, however, it is not impossible for a state to decide that it would be better, both for children and for the country, to give schools freedom to develop educational approaches that follow liberal education principles, whether within the state system or outside it, especially if evidence can be gathered to show the beneficial effects it is having.’

‘Whereas in pre-modern Western culture pride and self-respect were derived from involvement in family, community, work and religion, individuals are nowadays left with nothing but their individualism and inner experiences…When this is insufficient, many people attempt to find their salvation…in materialism and consumption, which have become the primary culturally accepted forms of meaning.’

‘Christianity from its beginnings has presented something new with regard to political life: a certain indifference, if I may put it that way, to the political regime. That is, it enjoins rendering unto Caesar the things that are Caesar’s, and unto God the things that are God’s, and hence obeying one’s rulers so long as they do not demand sin, especially idolatry. These injunctions are founded on the faith that the City of God rather than the City of Man is man’s ultimate destiny.’

‘Despite the different—and certainly debatable—approaches and priorities in specific policy areas, the fundamental objectives of conservative parties largely align. Public discourse and media representation in the West sometimes portray the self-determined policymaking of conservative governments in a polarized manner, focusing more on potentially divisive issues than on constructive dialogue.’