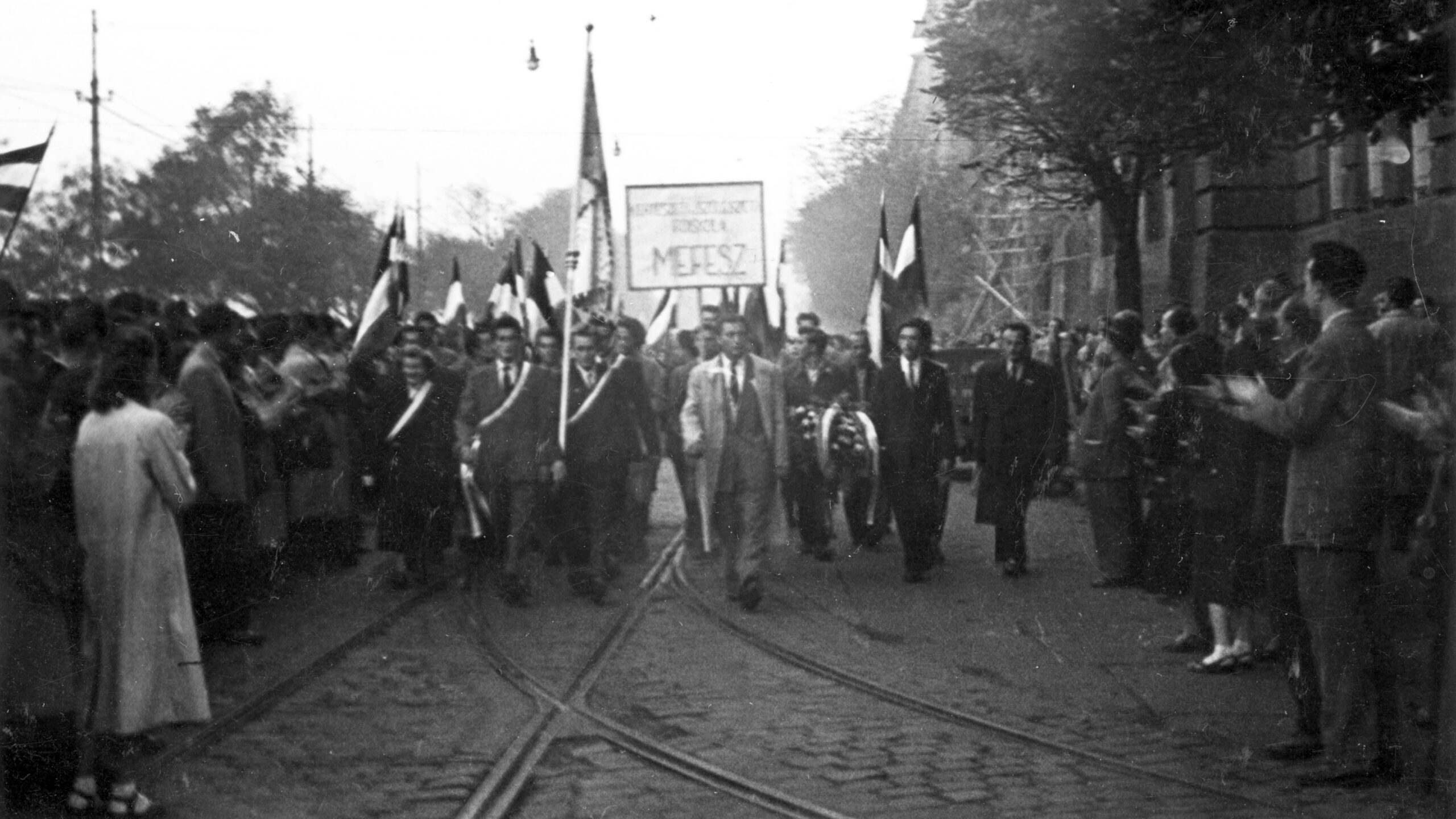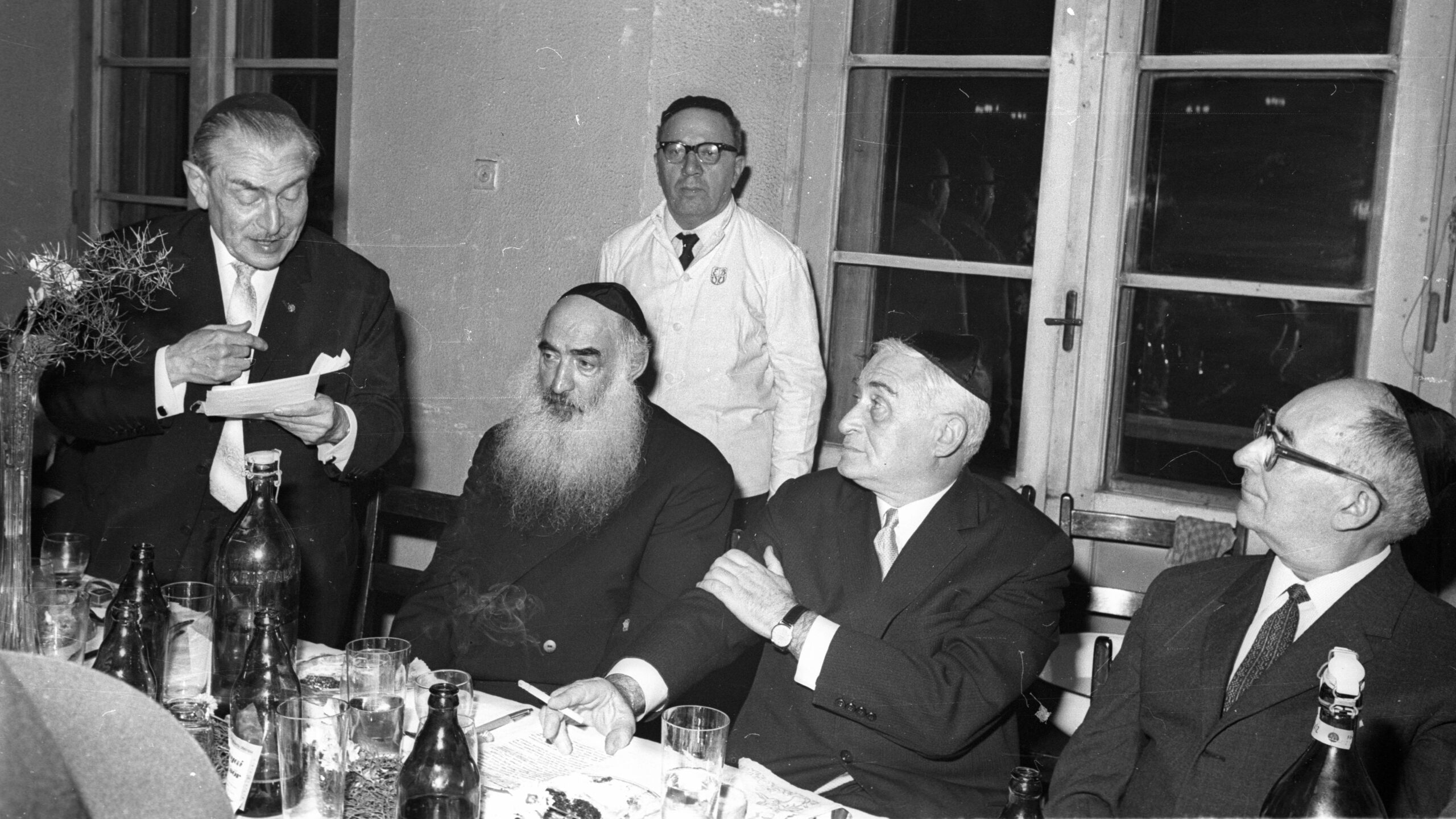
When Géza Seifert Stood Against the Party — A Forgotten Chapter of the 1956 Uprising
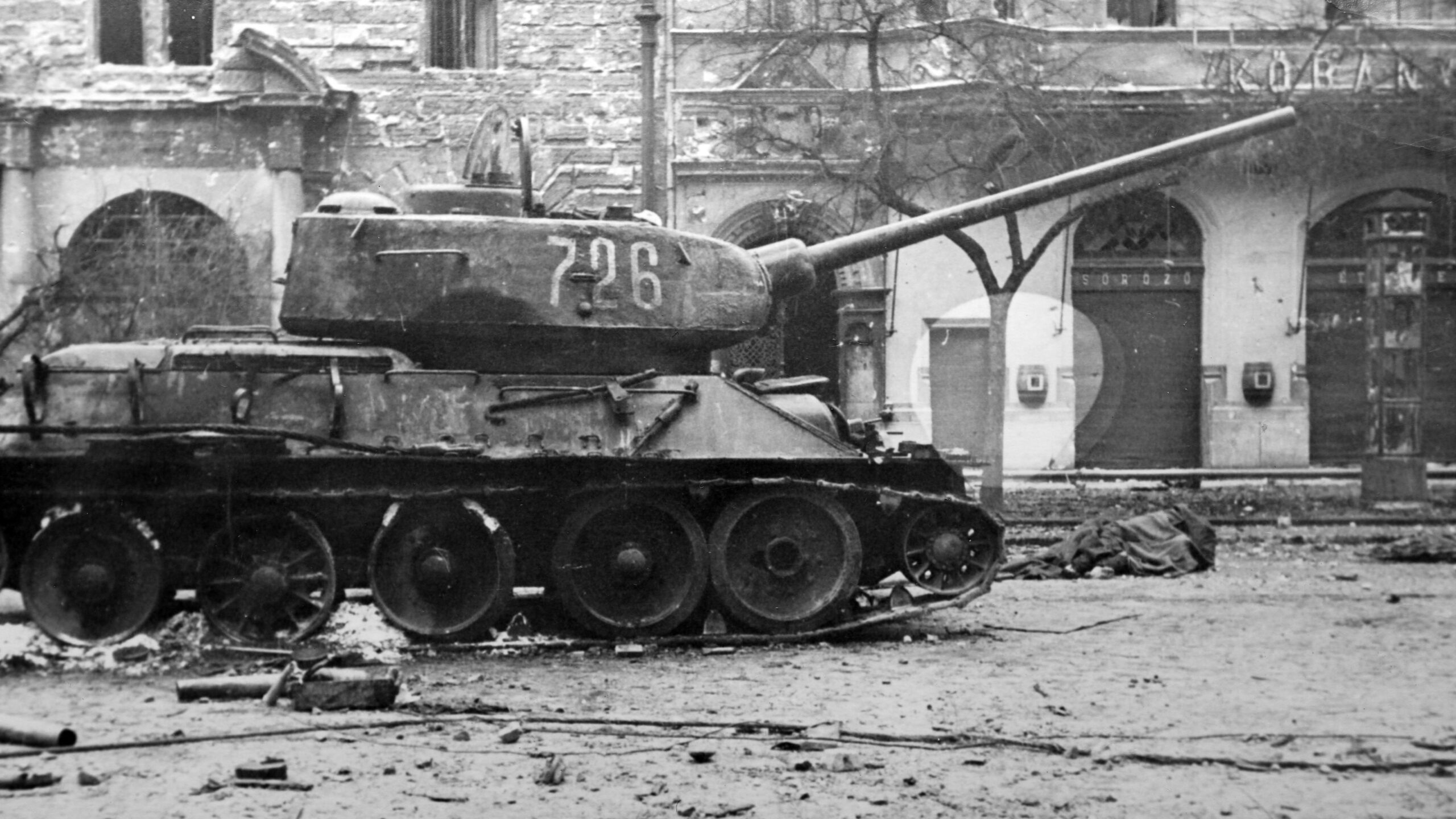
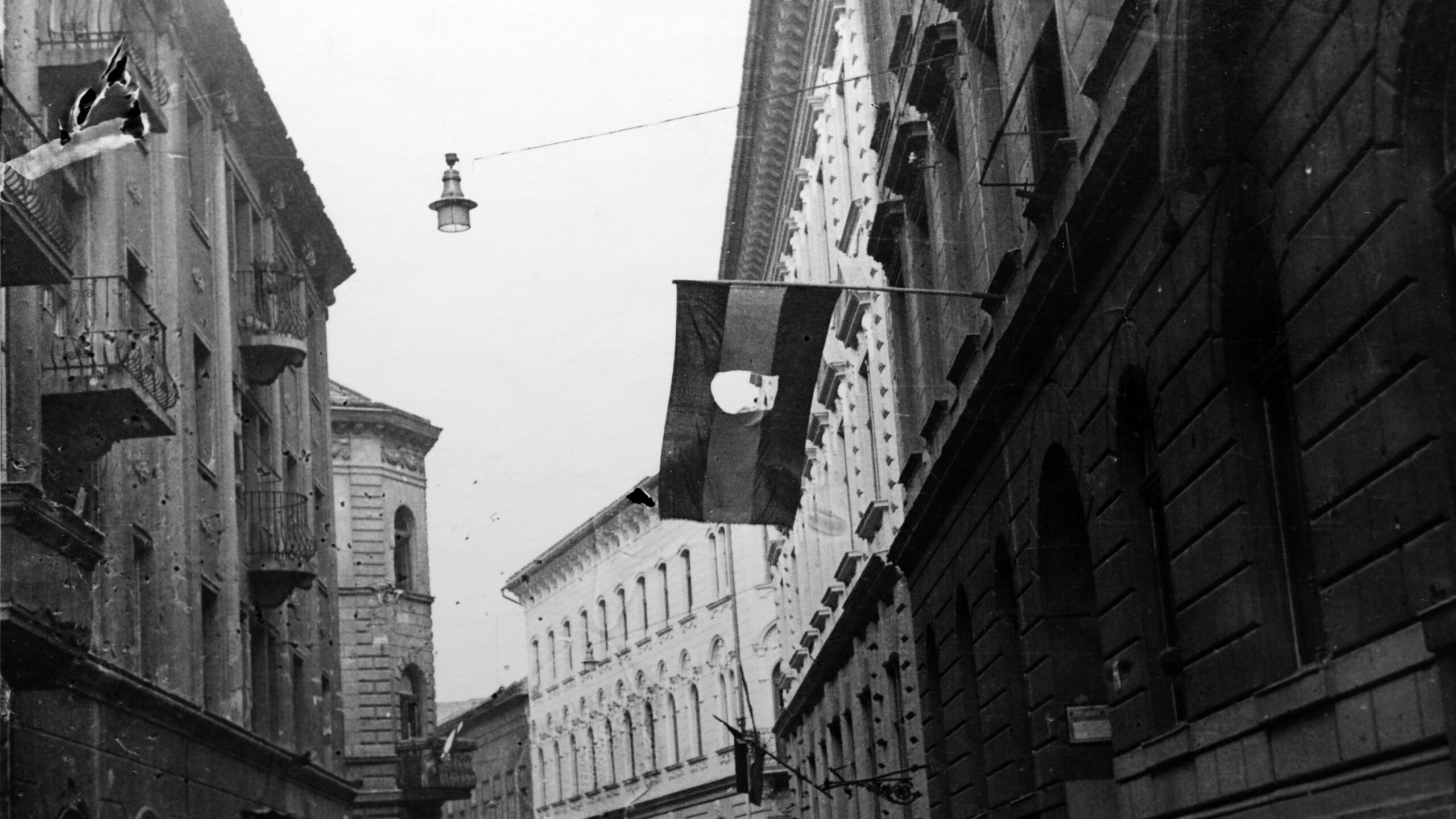
Although Géza Seifert later became a loyal Communist collaborator and President of the National Representation of Hungarian Israelites, he briefly led a ‘revolutionary committee’ within the Budapest Jewish community during the 1956 uprising—a role long forgotten and absent from scholarly accounts. This article revisits that moment, based on newly examined archival sources.